Your cart is currently empty!

The Ultimate Guide to Rapid Prototyping: Concept to Creation
•
Turning Ideas into Reality, Fast

Bringing a new product from concept to market can be a daunting journey. Traditional prototyping methods are often slow, expensive, and inflexible, leaving innovators frustrated. Rapid prototyping changes the game—it’s a fast-paced, iterative approach that allows designers and engineers to create, test, and refine products efficiently.
In this guide, we’ll explore what rapid prototyping is, the step-by-step process, key techniques, benefits, real-world applications, and how it stacks up against traditional methods. By the end, you’ll understand how to leverage rapid prototyping to accelerate innovation and minimize risk.
What is Rapid Prototyping?

Rapid prototyping is a process used to quickly fabricate a scale model or functional prototype of a product using three-dimensional computer-aided design (CAD) data. Unlike traditional prototyping methods, which may rely on handcrafting or molding, rapid prototyping utilizes digital fabrication technologies like 3D printing and CNC machining to create models fast and accurately.
The core advantage? You can test and iterate ideas without committing to full-scale production, saving time, cost, and resources.
The Rapid Prototyping Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Conceptualize and Design

Everything starts with an idea. Designers sketch initial concepts and develop detailed CAD models. Digital modeling allows for precise planning and easy adjustments before fabrication.
Step 2: Choose Your Method

Selecting the right prototyping technique depends on your materials, budget, and product requirements.
3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)

- FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling): Low-cost, ideal for basic prototypes.
- SLA (Stereolithography): High-detail prints, perfect for intricate designs.
- SLS (Selective Laser Sintering): Strong, functional prototypes with complex geometries.
CNC Machining
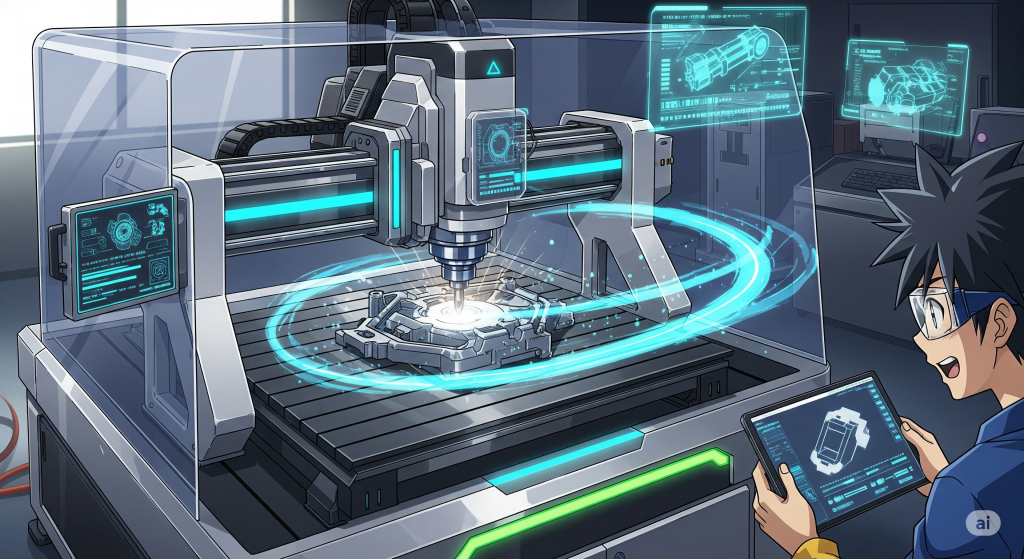
A subtractive process best for metal parts or components requiring tight tolerances. Excellent for functional testing.
Rapid Tooling & Injection Molding
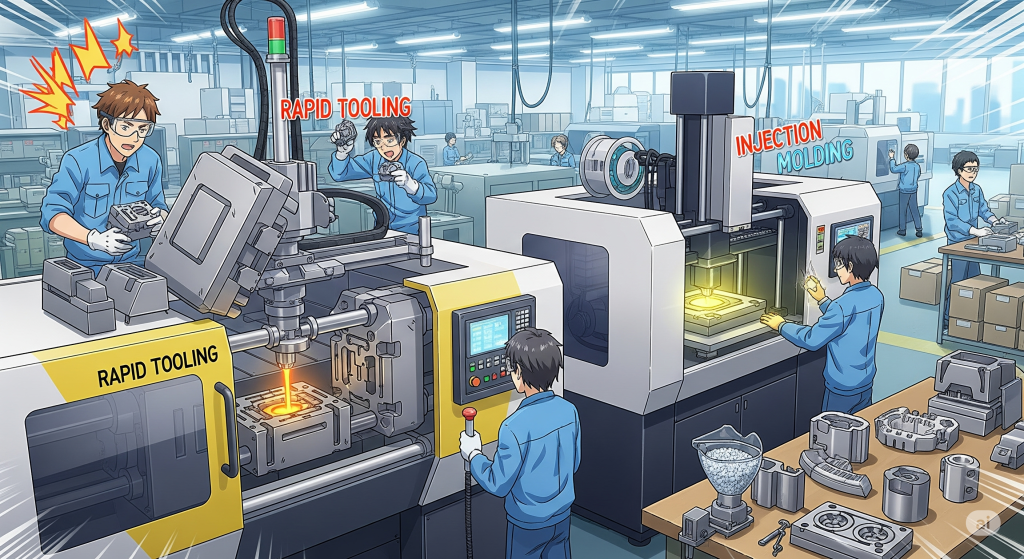
For low-volume production or more complex parts. Rapid tooling enables a prototype that mimics production processes closely.
Step 3: Fabricate the Prototype

Once the method is selected, the physical prototype is created. This is the stage where the design moves from screen to tangible object.
Step 4: Test and Validate

Gather feedback from stakeholders, engineers, and end-users. Check for functionality, usability, and overall design performance.
Step 5: Refine and Iterate

Rapid prototyping is cyclical. Adjust the design, test again, and improve. This iterative design process ensures a more polished final product.
Why is Rapid Prototyping Essential?

Accelerated Time-to-Market
Rapid prototyping shortens development cycles, allowing products to reach the market faster.
Cost Reduction
Early testing identifies flaws before expensive mass production, minimizing waste.
Improved User Experience
Prototypes enable early user feedback, ensuring the final product meets customer needs.
Enhanced Communication
Tangible models help teams and investors visualize concepts better than 2D drawings.
Risk Mitigation
Detect design flaws and engineering issues early, reducing potential failures in full-scale production.
Real-World Applications and Examples

Automotive: Prototyping car parts for fit, function, and safety tests.
Medical/Healthcare: Creating organ models for surgical planning or prototyping medical devices.
Consumer Goods: Testing product aesthetics and ergonomics, from electronics to packaging.
Aerospace: Developing lightweight, complex parts for high-performance applications.
Rapid Prototyping vs. Traditional Prototyping

| Feature | Rapid Prototyping | Traditional Prototyping |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Days to weeks | Weeks to months |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher upfront investment |
| Flexibility | High, easy iterations | Low, hard to modify |
| Materials | Wide range (plastics, metals) | Limited by manual methods |
| Complexity | Handles intricate designs easily | Complex designs are difficult |
Common Challenges and Solutions

Initial Cost: Equipment can be expensive. Solution: Use a rapid prototyping service to access technology without high upfront costs.
Material Limitations: Not all materials are available for every method. Solution: Carefully select materials based on product needs or combine techniques.
Lack of Expertise: Skilled operators are essential. Solution: Invest in training or outsource to experienced professionals.
Your Ideas, Faster and Smarter

Rapid prototyping is more than a manufacturing method—it’s a strategic approach that accelerates innovation, reduces risk, and enhances product quality. By embracing iterative design, digital fabrication, and modern prototyping techniques, you can bring your ideas to life faster and more efficiently than ever before.
Ready to turn your concept into a tangible product? Explore our rapid prototyping services today or download our free guide to choosing the right prototyping technique.
Leave a Reply